Category: Intellectual Nourishment

The Role of a Nutrition Support Team: a “best practice” in clinical nutrition1,2
Parenteral nutrition is the intravenous (IV) delivery of nutrients to critically and chronically ill patients who cannot eat by mouth or obtain enough nutrients through enteral nutrition alone. It can be a complicated process that requires an integrated team effort to ensure safe and effective delivery. Enter the Nutrition Support Team (NST). An NST is a multidisciplinary team made up of several healthcare professionals who work together to help meet the nutritional needs of their patients in many settings, including hospitals, long-term care facilities, and homes. Who are these healthcare professionals and what roles do each of them play in delivering nutrition support? Keep reading to find out.
“[An] NST has a central role in the management of patients with complex nutritional therapy in the inpatient and outpatient setting, during the hospital stay and beyond.”3
Physicians, dietitians, pharmacists, and nurses make up the Nutrition Support Team4,5:
-

Physicians most often lead the Nutrition Support Team. They must communicate with other members of the team and “engage in all aspects of direct care of patients’ nutritional needs.”4 They should be familiar with their patient’s nutritional status to provide the best care possible. In addition, they are responsible for writing an appropriate PN prescription.
-

Dietitians perform assessments to determine each patient’s individual nutritional needs. Once the assessment is complete, they communicate with the physician and recommend a customized nutrition care plan for their patient.
-

Pharmacists are integral members of the Nutrition Support Team in that they help improve the quality of care by making treatment and dosing recommendations and providing education to other healthcare professionals, patients, families, and caregivers. They are responsible for verifying and compounding PN orders, ensuring that the PN formula is appropriate and that the ingredients are compatible. In addition, they must make sure that PN solutions are properly labeled, delivered, and stored.
-

Nurses provide direct patient care. They obtain IV access and administer PN to their patients while maintaining infection control. They also monitor their patients and communicate any changes to the physicians who are managing their patients’ nutritional care. In addition, nurses provide education to patients and their families or caregivers.
“The key task of NSTs is to implement a comprehensive nutritional care system, so that every patient who could potentially benefit from nutritional support receives it rapidly, adequately, and with the highest standards of quality.”3
References: 1. Durfee SM, Adams SC, Arthur E, et al. A.S.P.E.N. Standards for Nutrition Support: Home and Alternate Site Care. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29(4):542-555. 2. Ukleja A, Gilbert K, Mogensen KM, et al. Standards for Nutrition Support: Adult Hospitalized Patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018;33(6):906-920. 3. Reber E, Strahm R, Bally L, Schuetz P, Stanga Z. Efficacy and Efficiency of Nutritional Support Teams. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1281. Published 2019 Aug 22. 4. What Is a Nutrition Support Professional?. ASPEN website. https://www.nutritioncare.org/what-is-a-NSP/. Accessed June 1, 2022. 5. Boullata JI. Overview of the parenteral nutrition use process. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36(2 Suppl):10S-13S.
2915-NP-08-06/22

A resource guide for all things parenteral nutrition (PN)
PN provides nourishment to critically ill and chronically ill patients of all ages. However, many of these patients feel overwhelmed by the prospect of adjusting to life on PN. The good news is that there are a number of organizations that support patients and caregivers throughout their unique PN journey. In addition, there are many reputable organizations for the healthcare community that help to facilitate the exchange of important scientific knowledge and best practices.
-

The Oley Foundation is “striving to enrich the lives of those living with home intravenous nutrition and tube feeding through education, advocacy, and networking.”1
The Oley Foundation provides a number of resources, including community enrichment programs, that support PN patients and their families. They are fierce patient advocates, and they connect patients with the educational and emotional support they need. They also provide resources for clinicians to help them better educate their patients and motivate them to engage in their own nutritional care and management.
-

Graham’s Foundation provides “support for every path along the journey of prematurity.”2
Whether you’re a parent of a preemie or you know someone with a premature infant, Graham’s Foundation provides support for those navigating the complications of prematurity of which gastrointestinal issues are common. Through Graham’s Foundation, preemie parents can explore resources that inspire hope and comfort, and they can connect with other parents who are going through a similar journey.
-

The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) works “to improve patient care by advancing the science and practice of clinical nutrition and metabolism.”3
ASPEN is a leading organization made up of healthcare professionals, including dietitians, nurses, pharmacists, physicians, scientists, and students, committed to “advancing the science and practice of clinical nutrition and metabolism.”3 From research to continuing education to evidence-based guidelines, ASPEN provides many resources to help clinicians deliver safe and effective PN.
-

The National Home Infusion Association’s (NHIA) mission is “to provide advocacy, education, and resources to the home and alternate site infusion community so the patients they serve can lead healthy, independent lives.”4
Many patients on PN are effectively able to manage their nutritional needs at home. NHIA is a leading authority in home infusion. They are an organization whose specific goal is to meet the needs of home and specialty infusion therapy communities and their patients to “help ensure the patient is receiving the best care possible.”4 They are committed to partnering with clinicians to improve nutritional care for patients receiving PN at home.
-

The North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) strives “to be a world leader in research, education, clinical practice and advocacy for pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition in health and disease.”5
NASPGHAN is a clinical organization made up of more than 2,600 pediatric gastroenterologists who share a common goal: to improve nutritional outcomes of young patients with various digestive disorders. NASPGHAN encourages communication and research to aid in the advancement of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition.
-

The Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) works “to secure the highest-quality care for all critically ill and injured patients.”6
SCCM is a nonprofit medical organization consisting of members who are “dedicated to promoting excellence and consistency in the practice of critical care.”6 SCCM offers guidelines and other clinical resources to help healthcare professionals provide optimal care to their sickest patients. SCCM also provides a variety of resources to patients and caregivers including a patient communicator app and an educational booklet to better their understanding of how to thrive after discharge from the hospital.7
As a global leader in clinical nutrition, we’re proud to work with all the wonderful organizations that make nutritional care a priority. Discover how we’re supporting patients with our innovations that nourish here.
References: 1. The Oley Foundation. The Oley Foundation website. https://oley.org. Accessed May 4, 2022. 2. Graham’s Foundation. Graham’s Foundation website. https://grahamsfoundation.org. Accessed May 4, 2022. 3. ASPEN: Leading the Science and Practice of Clinical Nutrition. ASPEN website. https://www.nutritioncare.org/About_ASPEN/ASPEN__Leading_the_Science_and_Practice_of_Clinical_Nutrition/. Accessed May 4, 2022. 4. NHIA. About Us. NHIA website. https://nhia.org/about-nhia/. Accessed May 4, 2022. 5. NASPGHAN. About Us. NASPGHAN website. https://naspghan.org/about/. Accessed May 4, 2022. 6. SCCM. About SCCM. SCCM website. https://www.sccm.org/about-sccm/. Accessed May 16, 2022. 7. SCCM. Patients & Family. SCCM website. www.sccm.org/MyICUCare/Home. Accessed May 16, 2022.
2795-NP-08-05/22

Dedicated to nourishing patients at every age and stage of life
Patients of all ages, from the oldest to the youngest, who are unable to meet their nutritional needs orally or enterally may require parenteral nutrition (PN). Those patients’ daily nutritional requirements are supplied intravenously with a PN solution, which is made up of water, energy (or calories), amino acids, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. But PN solutions aren’t all the same. As pioneers in clinical nutrition, we’re constantly striving to develop innovative PN products to help nourish critically and chronically ill patients at every age and stage of life—specifically, we develop alternative-oil lipid injectable emulsions (ILEs).
But you might ask, “What difference do fatty acids in PN make?” Well, it comes down to the clinical benefits and/or drawbacks of ILEs. The first ILEs developed were 100% soybean oil. However, soybean oil is made up of 50% linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid with pro-inflammatory properties.1 On the other hand, fish oil, which is one of the newer fatty acids to be used in PN, mostly consists of omega-3 fatty acids, which may have less pro-inflammatory effects.1 That’s why formulating ILEs with alternative lipid sources, like fish oil, has been a focus of ours.
Some of the “firsts” in the parenteral nutrition space to incorporate fish oil include Omegaven®, which is a 100% fish-oil ILE for pediatric patients with parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis. Another is SMOFlipid®, which is the first and only ILE to contain a unique blend of four oils. But what’s exciting is that SMOFlipid is now indicated for both adults and pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates, as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition.2 Now, patients of all ages have access to this unique blend of lipids:
-

Soybean oil 30% (omega-6)
Provides essential fatty acids -
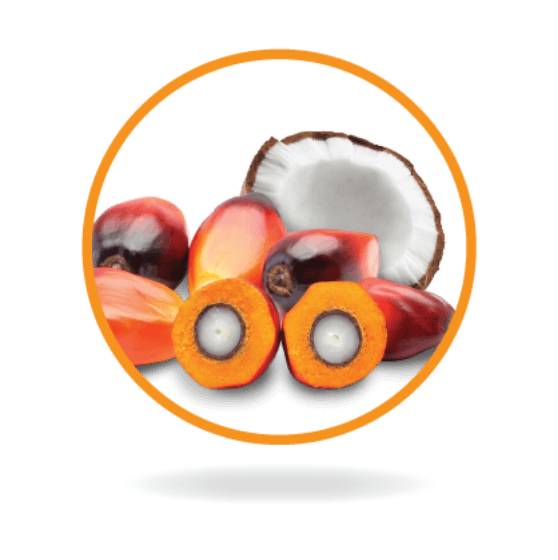

Medium-chain triglycerides 30%
A source of rapidly available energy3 -
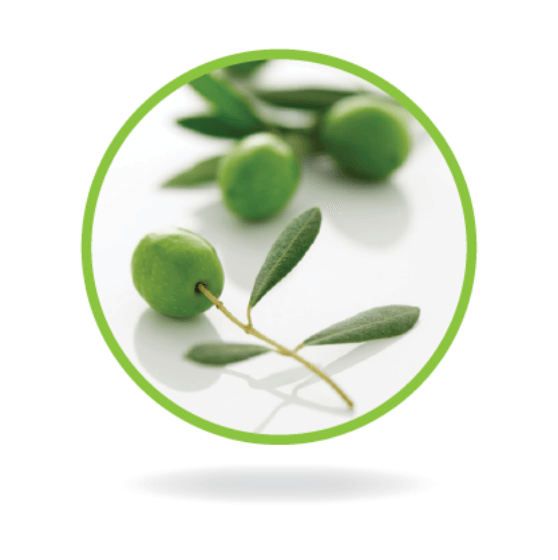

Olive oil 25% (omega-9)
Supplies monounsaturated fatty acids and contains small amounts of linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid -

Fish oil 15% (omega-3)
A source of omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA
With the expansion of SMOFlipid’s indication to include patients of all ages, now healthcare providers and parents of infants and children on parenteral nutrition at home have another option to help nourish even the youngest patients. Discover the SMOF difference at: www.FreseniusKabiNutrition.com/deliver
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SMOFlipid is indicated in adult and pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates, as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
For intravenous infusion only into a central or peripheral vein. Use a non-vented non-DEHP 1.2 micron in-line filter set during administration. Recommended dosage depends on age, energy expenditure, clinical status, body weight, tolerance, ability to metabolize and eliminate lipids, and consideration of additional energy given to the patient. The recommended dose for adults and pediatrics is shown in Table 1. For information on age-appropriate infusion rate, see the full prescribing information. SMOFlipid Pharmacy Bulk Package is only indicated for use in pharmacy admixture programs for the preparation of three-in-one or total nutrition admixtures. Protect the admixed PN solution from light.
Table 1: Recommended Adult and Pediatric Dosage
| Age | Nutritional Requirements | |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Recommended Dosage | Maximum Dosage | |
| Birth to 2 years of age (including preterm and term neonates) | 0.5 to 1 g/kg/day | 3 g/kg/day |
| Pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age | 1 to 2 g/kg/day | 3 g/kg/day |
| Pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age | 1 g/kg/day | 2.5 g/kg/day |
| Adults | 1 to 2 g/kg/day | 2.5 g/kg/day |
SMOFlipid is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to fish, egg, soybean, peanut, or any of the active or inactive ingredients, and severe disorders of lipid metabolism characterized by hypertriglyceridemia (serum triglycerides >1,000 mg/dL).
Clinical Decompensation with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and Infants: Acute respiratory distress, metabolic acidosis, and death after rapid infusion of intravenous lipid emulsions have been reported.
Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Increased risk in patients who received parenteral nutrition for greater than 2 weeks, especially preterm neonates. Monitor liver tests; if abnormalities occur consider discontinuation or dosage reduction.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Monitor for signs or symptoms. Discontinue infusion if reactions occur.
Risk of Infections, Fat Overload Syndrome, Refeeding Syndrome, Hypertriglyceridemia, and Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency: Monitor for signs and symptoms; monitor laboratory parameters.
Aluminum Toxicity: Increased risk in patients with renal impairment, including preterm neonates.
Most common adverse drug reactions (≥5%) from clinical trials in adults were nausea, vomiting, and hyperglycemia. Most common adverse drug reactions (≥5%) from clinical trials in pediatric patients were anemia, vomiting, increased gamma-glutamyltransferase, and nosocomial infection.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176, option 5, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use SMOFlipid safely and effectively. Please see full prescribing information, for intravenous use at www.FreseniusKabiNutrition.com/SMOFlipidPI.
References: 1. Vanek VW, Seidner DL, Allen P, et al. A.S.P.E.N. position paper: clinical role for alternative intravenous fat emulsions. Nutr Clin Pract. 2012;27:150-192. 2. SMOFlipid Prescribing Information, Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC. 2022. 3. Deckelbaum RJ, Hamilton JA, Moser A, et al. Medium-chain versus long-chain triacylglycerol emulsion hydrolysis by lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase: implications for the mechanisms of lipase action. Biochemistry. 1990;29(5):1136-1142.
2675-OMEG-08-06/23
Steps to safe parenteral nutrition preparation and administration
Parenteral nutrition (PN). It’s a valuable source of nutrition for critically and chronically ill patients who are unable to receive the nutrients they need via the oral or enteral route. It’s also a complex process with room for errors. It certainly takes a “village”—an interdisciplinary approach—involving multiple healthcare professionals and several steps to ensure its safe delivery and administration.1 And it all starts with assessing your patient’s need for PN.
-

1. Assessment1:
During this first step in the PN use process, the dietitian and/or nutrition support team will:- Review patient data
- Conduct a nutrition assessment including estimation of nutrient requirements
- Determine nutrition intervention and nutrition prescription based on therapy goals and clinical condition
- Communicate with the prescriber
-

2. Prescription1:
When determining an appropriate prescription for PN, a clinician must decide2:- Appropriate use
What’s my patient’s indication for the use of PN? - IV access
How long will my patient be on PN? Will they need a peripheral line or a central line? - PN ingredients
How much protein, lipids, and dextrose will my patient need? What about vitamins, trace elements, electrolytes, and total volume? - PN instructions
What’s the infusion rate and the start and stop times?- A safety tool in prescribing PN is to use a standardized PN order format and sequence of PN components
- Appropriate use
-

3. Review, verification, and transcription1,3:
Once the PN is prescribed, the pharmacist will review and verify that the received order is appropriate before any preparation or compounding begins. This process includes two steps:- A clinical review to verify that the indication and the dosing of each nutrient is appropriate for the patient
- A pharmaceutical review to verify the compatibility of the PN components and the stability of the final preparation
After these steps are completed, the pharmacist will then transcribe the PN order from handwritten (although not recommended), printed, or CPOE system to the automated compounding device (ACD). An additional independent double check is performed to ensure accuracy of the PN prescription.
-

4. Preparation, compounding, and dispensing1,3:
Once the prescription is deemed appropriate, the pharmacist and pharmacy technician will prepare and compound the PN following sterile compounding techniques. Before the final preparation goes out the door to be dispensed, the pharmacist must assure that it is properly labeled, delivered, and stored. -
5. Administration1:
Finally, the PN admixture has made it from the pharmacy to the nurse or caregiver who is responsible for its safe administration. They should be knowledgeable and acquire the skills needed to verify the correct PN order, avoid administration errors, and maintain infection control. -

6. Monitoring1:
The final step in the PN use process is monitoring. An experienced nutrition care team will closely monitor their patient to prevent and detect any complications that may occur throughout their patient’s journey with PN.
For more information on the safe use of the Fresenius Kabi Nutrition portfolio, please reach out to a PN Specialist or click here to access an abstract by pharmacist Dr. Joseph I. Boullata reviewing the PN use process.
Click here for more expert content by Dr. Boullata and Dr. Jay Mirtallo on PN safety
Click here to view ASPEN’s PN Resources.
References: 1. Boullata JI. Overview of the parenteral nutrition use process. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36(2 Suppl):10S-13S. 2. Ayers PA, et al. ASPEN Parenteral Nutrition Handbook. 2014;111-132. 3. Boullata JI, Holcombe B, Sacks G, et al. Standardized Competencies for Parenteral Nutrition Order Review and Parenteral Nutrition Preparation, Including Compounding: The ASPEN Model. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016;31(4):548-555.
2284-CORP-08-11/21

Can I manage my own parenteral nutrition? Tips to help you flourish on parenteral nutrition at home
You’re going home on parenteral nutrition. We know you’re happy, but you’re probably also nervous and have some questions like “Can I administer my own parenteral nutrition?” and “Can I still do the things I enjoy?”
We get it; you’re not alone. Many people require parenteral nutrition at home for many different reasons. In fact, more than 25,000 patients manage their parenteral nutrition within the comfort of their own homes.1 Let’s talk about some tips that can help you feel more confident throughout your journey with home parenteral nutrition.
-
Understand and get comfortable with your own parenteral nutrition regimen2:
Your healthcare team will provide training on how to safely administer PN at home and avoid complications. This includes learning how to properly store and prepare your bags, how to inject additives into your bags, how to attach the tubing to your catheter, and how to use the IV pump. If you have questions, reach out to your nurse, pharmacist, dietitian, or healthcare team. They’re there to help you feel as confident as possible in administering your own parenteral nutrition. Your healthcare team will also talk with you about monitoring your weight, hydration status, and any laboratory measurements that may be needed.
-
Establish an infusion schedule that’s convenient for you2:
Home parenteral nutrition infusions typically take 8 to 12 hours a day.3 If you can sleep well while you’re hooked up to an IV, you may consider a nighttime schedule. However, if you cannot sleep while infusing, a daytime schedule may be your best option. Work with your healthcare team to determine your home infusion schedule.
-
Learn how to care for your IV line2:
During your home PN training, you will learn how to take care of your IV line. This training is very important in preventing infection. Ask your doctor or nurse for specific instructions on how to properly care for your line.
-
Monitor your side effects2:
Like with any medication, parenteral nutrition comes with its own risks and possible side effects. Your healthcare team will teach you about the side effects of parenteral nutrition and how to monitor for them. Knowing how your body responds to your infusions will help you recognize any side effects that may occur along the way. If you experience side effects that are bothersome or won’t go away, contact your doctor immediately as they may decide to adjust your regimen as necessary.
-
Educate your friends and family2:
Your friends and family are your biggest fans. Teaching them about parenteral nutrition, why you need it, and even how to administer it can help them understand the challenges you’re facing. And when they understand those challenges, they will be able to support you even more in the ways that you need most.
-
Seek out a support group2:
Support groups, such as the Oley Foundation, bring together people with similar therapy and nutritional needs. These organizations serve as a beneficial resource to individuals on parenteral nutrition. Click here to visit the Oley Foundation support group page.
Remember, at any point in your nutrition journey if you have questions or concerns, contact your healthcare team for guidance and support.

Here at Fresenius Kabi we aim to inspire hope in critically and chronically ill patients by delivering innovations that nourish at every age and stage—from hospital to home. To explore our comprehensive portfolio of parenteral nutrition products, click here. Remember to keep checking our Intellectual Nourishment blog for updated content.
References: 1. Mundi MS, Pattinson A, McMahon MT, Davidson J, Hurt RT. Prevalence of Home Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition in the United States. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(6):799-805. 2. Shieh S. 10 Tips for Adjusting to Your Life With TPN (Total Parenteral Nutrition). AmeriPharma Specialty Care. https://ameripharmaspecialty.com/10-tips-for-adjusting-to-your-life-with-tpn-total-parenteral-nutrition/. October 7, 2021. Accessed February 3, 2022. 3.Kirby DF. Improving outcomes with parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012;8(1):39-41.
2488-NP-08-02/22

What good are guidelines and recommendations?
Without guidelines and recommendations, we would live in chaos! We would be back in the Wild West making wild guesses and assumptions. So we have guidelines and recommendations. Not hard and fast like laws, guidelines and recommendations do offer some leeway to use one’s clinical judgment. But because guidelines and recommendations are based on the strongest available scientific evidence, they shouldn’t be ignored. But what good are they really? Let’s look at parenteral nutrition guidelines and recommendations for an example. The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) is a great resource for guidelines and recommendations.
-
What do the guidelines say about nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient? The ASPEN-SCCM clinical guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient offer basic recommendations that are supported by review and analysis of the current literature, other national and international guidelines, and a blend of expert opinion and clinical practicality.
-
When is parenteral nutrition appropriate? Consensus recommendations by Worthington P, et al, aim to delineate appropriate parenteral nutrition use and promote clinical benefits while minimizing the risks associated with the therapy. Read the full document.
-
What is appropriate dosing for parenteral nutrition? Persistent shortages of parenteral nutrition components have led to a tendency of practitioners to provide less than adequate dosing, which can lead to nutrient deficiencies that impair growth and healing. This document provides the requirements and recommendations for dosing of nutrients for a complete parenteral nutrition prescription.
-
What about alternative lipid injectable emulsions (ILEs)? There are expert recommendations regarding the use of alternative ILEs in surgical and critical care patients. The 2018 Lipids in Parenteral Nutrition summit involved a panel of experts in clinical nutrition, lipid metabolism, and pharmacology to develop consensus statements regarding the use of alternative ILEs.
-
How do I achieve photoprotection for parenteral nutrition? A position paper by Robinson DT, et al, reviews the scientific literature on the formation of quantifiable peroxides and other degradation products when parenteral nutrition admixtures and lipid injectable emulsions are exposed to light and reports adverse clinical outcomes in premature infants exposed to parenteral nutrition.
Whether you have a question on dosing or storage or delivery, there’s probably a clinical recommendation for it. The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) has guidelines and consensus recommendations that are based on literature and practices to help guide the use of parenteral nutrition to minimize errors associated with parenteral nutrition therapy. But that’s just one resource. There are also the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN), the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN), the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM).
Whether a patient is in the hospital, a long-term care facility, or is being discharged to home, these guidelines and recommendations exist to help guide the safe and effective use of parenteral nutrition. As a pioneer of clinical nutrition, we believe it’s of the utmost importance to stay on top of these guidelines. That’s why we post any updates and links to these professional societies on our Resources page.
2285-CORP-08-11/21

The 411 on parenteral nutrition
Before we dive into our innovations that nourish, let’s start with the basics.
What is parenteral nutrition? Well, it’s nutrition. It’s nourishment…but not as you may know it. To be more technical, it’s the intravenous administration of nutrition, which may include protein, carbohydrates, fat, minerals and electrolytes, vitamins, and other trace elements.1 When patients are unable to maintain good nutritional status by mouth or through tube feeding formula, they may need parenteral nutrition.1 There are a variety of diseases or conditions that prevent patients from being able to eat, digest, or absorb the nutrition they need, including critical illness, bowel obstruction, GI fistulas, and severe acute pancreatitis.1 In 2014, there were about 34,000 U.S. hospitalized patients receiving parenteral nutrition.2
Did you know that parenteral nutrition can be used outside of the hospital? Patients can receive parenteral nutrition in long-term care facilities and at home. In fact, about 25,000 patients receive parenteral nutrition at home.3 And patients can live well on parenteral nutrition, whether they need it for a short time or a long time.1
What should you know about parenteral nutrition?
-

Rapid absorption.
Because parenteral nutrition is administered intravenously, it bypasses the gastrointestinal tract, meaning it doesn’t have to be digested before being absorbed by the blood.1 The parenteral nutrition solution is delivered immediately into the bloodstream to exert its therapeutic effects.4
-

Nutritional support for all ages.
Patients of all ages, including infants (yes, infants!), may receive parenteral nutrition.1 According to the 2014 National Inpatient Survey data (the latest available statistics), patients received parenteral nutrition in over 290,000 hospital stays.1 You may be surprised to know that children and newborns made up about 43% of those.1
-
There are choices!
There are a lot of parenteral nutrition products available on the market today. And as a pioneer in clinical nutrition, we’re always speaking with experts in the field to find new ways to fulfill the nutritional needs of patients who need parenteral nutrition. We specialize in innovations that help nourish critically and chronically ill patients in a variety of clinical settings. From lipid injectable emulsions to three-chamber bags, our products are designed to help your patients flourish from hospital to home.
To explore our comprehensive portfolio of parenteral nutrition products, click here. Remember to keep checking back for more updates!
References: 1. What is Parenteral Nutrition? American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Accessed September 23, 2021. http://www.nutritioncare.org/about_clinical_nutrition/what_is_parenteral_nutrition/. 2. John J, Seifi A. Total parenteral nutrition usage trends in the United States. J Crit Care. 2017;40:312-313. 3. Mundi MS, Pattinson A, McMahon MT, Davidson J, Hurt RT. Prevalence of Home Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition in the United States. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(6):799-805. 4. Le J. Drug Administration. Merck Manual Consumer Version. Revised October 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/drugs/administration-and-kinetics-of-drugs/drug-administration.
2284-CORP-08-11/21