One-of-a-kind blend of 4 oil sources1
Designed to provide a source of calories and essential fatty acids (EFAs) for parenteral nutrition (PN), SMOFlipid is the FIRST and ONLY 4-oil lipid injectable emulsion (ILE) with a well-established safety and tolerability profile.1 It has been administered to more than 7 million patients worldwide.*
*Data on file 4/1/25.

SMOFlipid is indicated for daily lipid dosing1
Lipids are a key part of a PN regimen, offering EFAs and serving as an alternative energy source to reduce reliance on dextrose, helping to minimize complications from excessive dextrose use, such as5,6:
- Hepatic steatosis
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Hyperglycemia-induced compromised immune function
- Metabolic stress
- Fever
SMOFlipid for adults has specific dosing recommendations.1
- Protect the admixed PN solution from light
- Use a non-vented, non-DEHP 1.2 micron in-line filter set during administration
Recommended dosage depends on age, energy expenditure, clinical status, body weight, tolerance, ability to metabolize and eliminate lipids, and consideration of additional energy given to the patient.1
Do not exceed the maximum infusion rate of 0.5 mL/kg/hour in adults.1
| Age | Nutritional Requirements | Direct Infusion Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended Initial Dosage and Maximum Dosage | Initial | Maximum | |
| Adults | 1 to 2 g/kg/day not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day* |
0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes | 0.5 mL/kg/hour |
*Daily dosage should not exceed a maximum of 60% of total energy requirements.
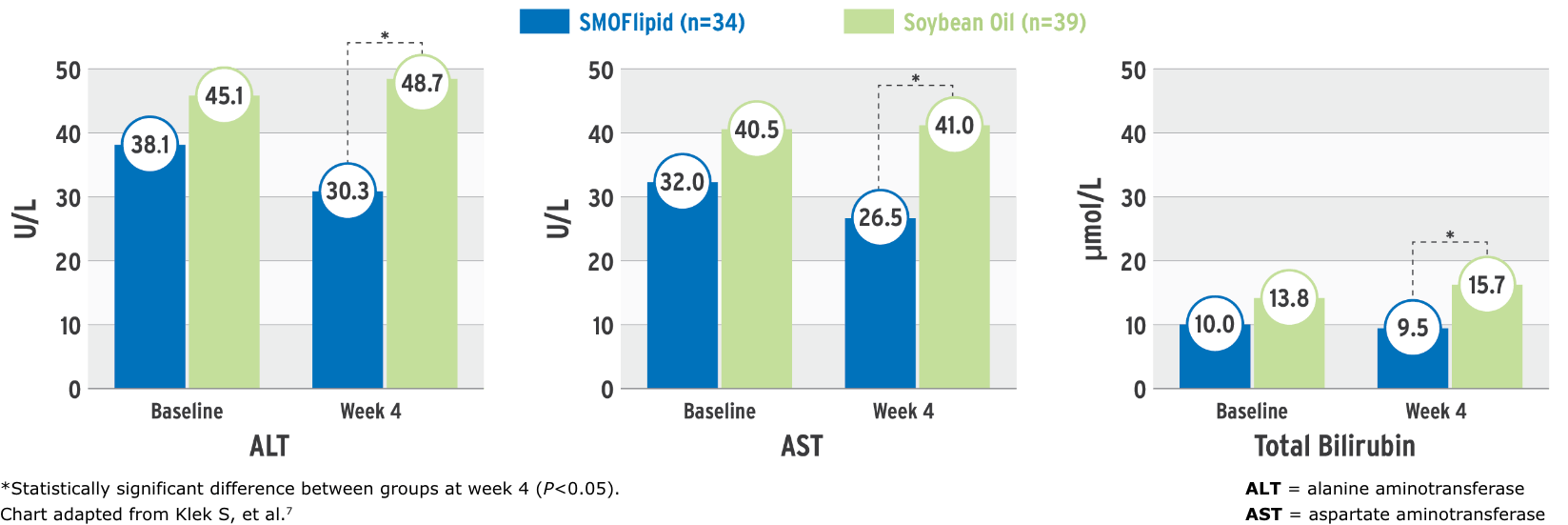
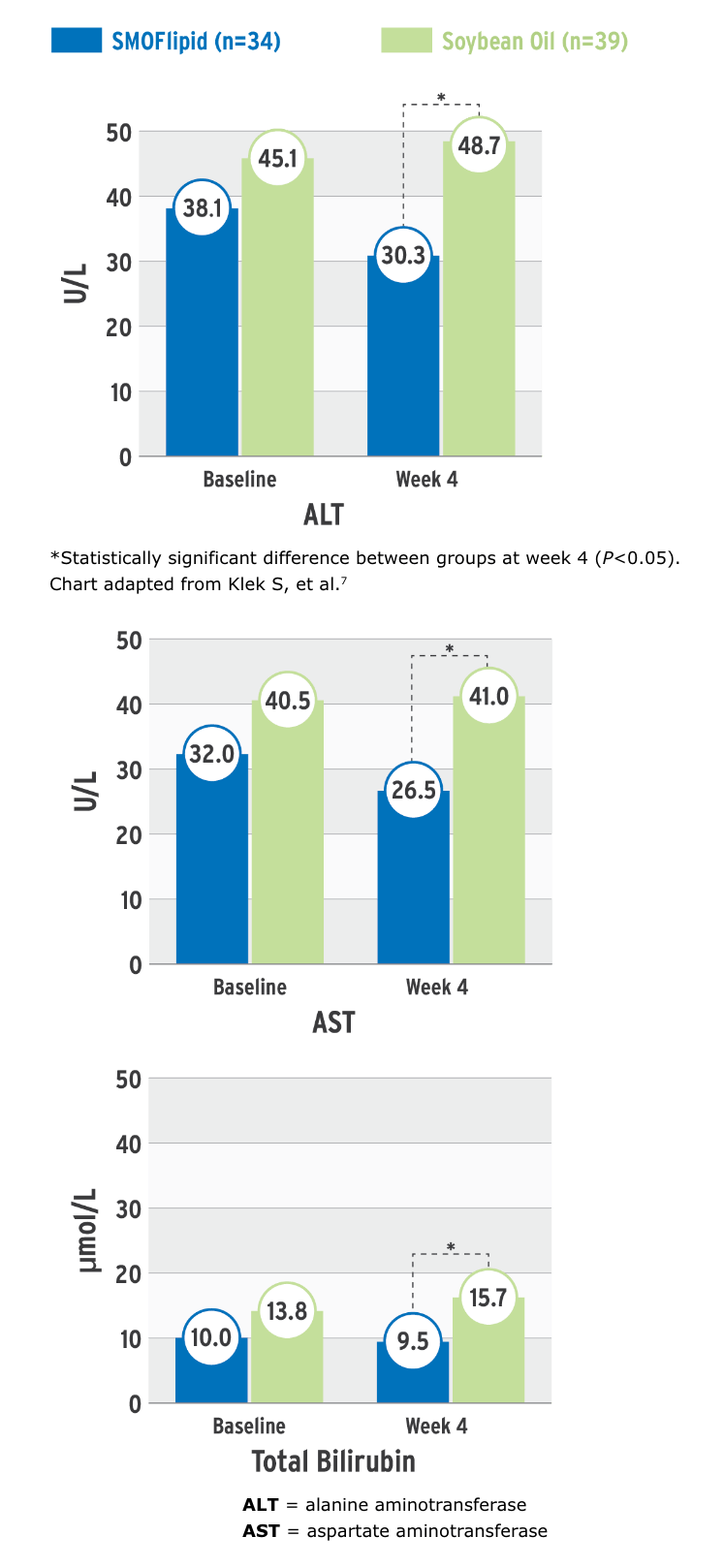
Effect on liver function parameters7
Each oil has characteristics which provide a unique blend. A clinical study observed SMOFlipid’s effect on liver function parameters7:
Parameters of Liver Function at Baseline and at Week 4
This randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter study compared PN containing SMOFlipid or an soybean oil (SO) emulsion in intestinal failure patients requiring long-term PN. Seventy-three patients (n=34 in SMOFlipid group and n=39 in the SO group) received PN with either lipid emulsion and were monitored for 4 weeks.7
- PN intake was similar in both groups: 1.3 g/kg/d ILE, 3 g/kg/d dextrose, 1.2 g/kg/d amino acids; infusion occurred 10-24 hr/d, 5-7 days per week7
- After 4 weeks, the mean concentrations of ALT, AST, and total bilirubin were significantly lower in the SMOFlipid group than the comparator group (statistical significance was set at P<0.05); there was no significance for change within treatment groups7
Two on-label adult clinical trials did not show a difference in liver parameters.*
*Data on file.
Monitor liver tests; if abnormalities occur, consider discontinuation or dosage reduction.1

Indication
SMOFlipid is indicated in adult and pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates, as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.1
SMOFlipid resources
Explore additional SMOFlipid materials by visiting our Resource Center.
For Consumers
SMOFLIPID® (lipid injectable emulsion USP), for intravenous use
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is SMOFlipid?
- Indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
- The hourly infusion rate in pediatrics should not exceed 0.75 mL/kg/hour and 0.5 mL/kg/hour in adults.
SMOFlipid should not be received by patients who have:
- A known allergy to fish, egg, soybean, or peanut, or to any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid.
- Abnormally high levels of lipid (triglycerides) in the blood.
SMOFlipid may cause serious side effects including:
- Serious Adverse Reactions with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and Infants: Strictly follow the recommended total daily dosage and do not exceed the maximum infusion rate. If poor clearance of fats occurs, the infusion should be stopped, and a medical evaluation started.
- Risk of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease (PNALD) may progress to liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver with scarring and cirrhosis.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you are experiencing an allergic reaction.
- Fat Overload Syndrome, Refeeding Syndrome, Elevated Triglycerides (Hypertriglyceridemia): Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of early infection and blood levels.
Monitoring/Laboratory Tests: The content of vitamin K may interfere with blood clotting activity of medications.
For Consumers
SMOFLIPID® (lipid injectable emulsion USP), for intravenous use
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is SMOFlipid?
- Indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
- The hourly infusion rate in pediatrics should not exceed 0.75 mL/kg/hour and 0.5 mL/kg/hour in adults.
SMOFlipid should not be received by patients who have:
- A known allergy to fish, egg, soybean, or peanut, or to any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid.
- Abnormally high levels of lipid (triglycerides) in the blood.
SMOFlipid may cause serious side effects including:
- Serious Adverse Reactions with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and Infants: Strictly follow the recommended total daily dosage and do not exceed the maximum infusion rate. If poor clearance of fats occurs, the infusion should be stopped, and a medical evaluation started.
- Risk of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease (PNALD) may progress to liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver with scarring and cirrhosis.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you are experiencing an allergic reaction.
- Fat Overload Syndrome, Refeeding Syndrome, Elevated Triglycerides (Hypertriglyceridemia): Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of early infection and blood levels.
Monitoring/Laboratory Tests: The content of vitamin K may interfere with blood clotting activity of medications.